why is bicarbonate low in diabetic ketoacidosis Ketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm
Imagine suddenly feeling extremely thirsty, experiencing abdominal pain and nausea, and feeling lethargic. You might be suffering from diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). It’s a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if left untreated. DKA happens when your body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. This occurs when your insulin levels drop and blood sugar spikes, and can cause a range of symptoms, from excessive thirst and urination to confusion and even coma. To understand why DKA is important, you must first know about the causes. One of those is hyperglycemia, or very high blood sugar levels. This occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin – a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels – or when insulin doesn’t work properly. Without insulin, the body cannot use glucose for energy. As a result, it breaks down fat instead, producing ketones. In addition to hyperglycemia, dehydration can also trigger DKA. When blood ketone levels rise, the body works hard to get rid of them through urine, causing water loss and dehydration. If not treated promptly, DKA can lead to serious complications, such as cerebral edema – swelling in the brain – and cardiac arrest. Fortunately, it can be treated with insulin to lower blood glucose levels, hydration to replace fluids lost through excessive urination, and electrolyte replacement to regulate the body’s chemical balance. The key to avoiding DKA is to keep blood sugar levels within a normal range. Eating a healthy diet, taking medication as directed, and exercising regularly can help. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly can also alert you to potential problems before they develop into an emergency. Remember that diabetic ketoacidosis can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. If you experience any symptoms, including excessive thirst and urination, abdominal pain, nausea, confusion, or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately. With proper treatment and care, you can manage your diabetes and avoid complications like DKA. Be vigilant about your health and work with your healthcare team to ensure you stay in control of your diabetes and live a healthy, fulfilling life. 
Aldosterone In Dka
When it comes to DKA, aldosterone plays a role in preventing the body from losing too much potassium. This is especially important because high levels of ketones can cause potassium to leave the body too quickly, leading to a dangerous condition called hypokalemia.
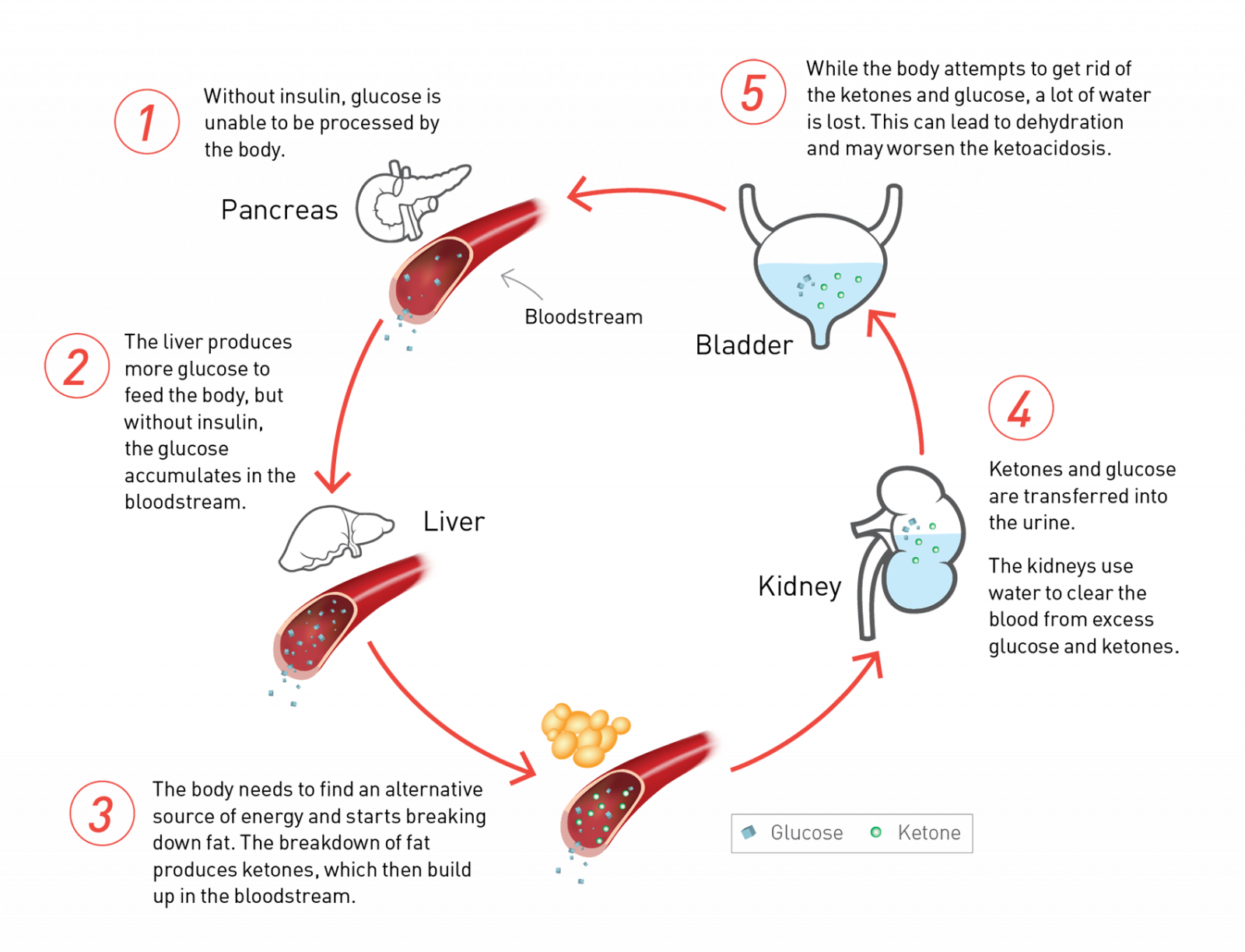 Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
DKA is a medical emergency that requires urgent treatment. It can occur in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, but it’s more common in people with type 1. Early recognition and prompt treatment of DKA can prevent serious complications.
If you are searching about Why Is Bun Elevated In Ketoacidosis | DiabetesTalk.Net you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pics about Why Is Bun Elevated In Ketoacidosis | DiabetesTalk.Net like How Does Ketoacidosis Work | DiabetesTalk.Net, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Why should it matter to me? | Nipro and also Aldosterone In Dka | DiabetesTalk.Net. Read more:
Why Is Bun Elevated In Ketoacidosis | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetestalk why bun potassium
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetestalk why bun potassium
Aldosterone In Dka | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin symptoms figure signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin symptoms figure signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Why Should It Matter To Me? | Nipro
 www.nipro-group.comketoacidosis dka diabetes nipro matter knowledge studying icu
How Does Ketoacidosis Work | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm
diabetestalk.netketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm
Why Is Bicarbonate Low In Diabetic Ketoacidosis? | DiabetesTalk.Net
 diabetestalk.netdiabetestalk bicarbonate
diabetestalk.netdiabetestalk bicarbonate
Ketoacidosis diabetic diabetes type ketosis pediatric dka starvation population insulin symptoms figure signs aldosterone diabetestalk quizlet sign. Ketoacidosis diabetic bicarbonate sodium diabetestalk nejm. How does ketoacidosis work